WHAT IS LAPAROSCOPY? LAPAROSCOPIC OPERATIONS IN UROLOGY.
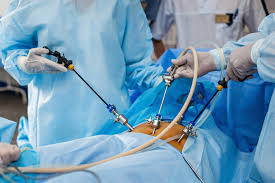
Laparoscopic operation is a modern, minimally invasive (that is, without a large incision) surgical method. In it, the doctor in the patient's abdomen or the organs in the pelvic region using a special instrument called a laparoscope and performs the operation.
🔍 How is laparoscopy performed?
A small incision (usually 0.5–1 cm) is made in the abdomen. the doctor sees the internal organs through the monitor. Necessary surgical instruments is inserted through another small incision.
When the operation is finished, the gas is released and the incisions are sutured.
📌 What conditions are used?
- Gall bladder removal (cholecystectomy)
- Appendix removal
- Ovarian cyst
- Uterus or ovary removal
- Endometriosis, infertility tests
- Urological diseases
✅ Advantages:
- Small incision - less blood loss
- Quicker recovery (usually 2-7 days)
- Less pain
- Hardly left a scar
- Hospital stay duration is short
Laparoscopic operations in urology - this is a method of treatment of diseases related to the urinary tract and genitals through small incisions using a laparoscope. This method causes less pain, faster recovery, and less scarring compared to traditional surgery.
🔬 The most common laparoscopic operations in urology:
Nephrectomy - kidney removal. Complete (total)
Partial (only tumor or damaged part)
- Pyeloplasty - kidney and urine the narrowed area between the path (ureter) (for example, in the narrowing of the ureteropelvic joint).
- Ureterolithotomy - removal of a large stone stuck in the urinary tract.
- Varicocelectomy - treatment of the enlargement of veins around the testicle (varicocele).
- Orchiectomy - removal of the testicle (in tumors or trauma).
- Prostatectomy – removal of the prostate (usually in case of cancer).
- Removal of kidney cysts – kidney cysts are cut out through a laparoscope.
✅ Advantages:
- Less blood loss
- Less pain
- Quick recovery (you can go home in 2-5 days)
- Esthetic scar (a small scar remains)
- Less risk of infection
⚠️ Note:
Laparoscopic surgery is not always possible. For example, open surgery is recommended for patients with very large tumors, previous major surgeries, or certain cardiovascular problems.



