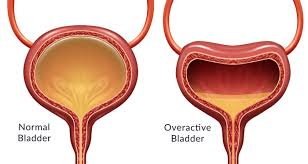
OVERACTIVE BLADDER (OAB-OVERACTIVE BLADDER) What is it?
Overactive bladder is the name of a group of bladder symptoms. There are three main symptoms:
- Feeling that you need to urinate,
- The need to urinate often (frequently), usually day and night (nocturia).
- Sometimes incontinence, which is urine leakage.
With an overactive bladder, you have to empty your bladder. you feel you need - even if it's not complete. You feel the urge to urinate again even though you have just passed urine. You cannot control or ignore this feeling and it happens to you more than it should. Sometimes when urinating, the bladder muscle may feel like it is contracting to empty the bladder, but the muscle may not actually be contracting. If you feel like you "need to go" eight or more times a day and night, or you are afraid of leaking urine, you may have an OVERACTIVE BLADDER.
SYMPTOMS:
Urgency: This is the main symptom of an OVERACTIVE BLADDER. This is a strong (urgent) need to urinate that cannot be ignored. When people with this disease feel "I want to pee" if a toilet cannot be found immediately, they are afraid of leaking urine.
Urine Leakage: Sometimes an ACTIVE BLADDER causes urine to leak before going to the toilet. This is called urge incontinence. Some people may have a few drops, while others may have a sudden leak.
Urine frequency: AN OVERACTIVE BLADDER can cause people to go to the bathroom many times during the day. Experts say frequent urination is having to urinate more than eight times in 24 hours.
Waking up to urinate at night: AN ACTIVE BLADDER can wake a person up to urinate several times a night. This is called nocturia.
An OVERACTIVE BLADDER has no pain. If you experience pain when urinating, you may have another problem, a urinary tract infection (UTI).
TREATMENT
There are several things you can do to manage an OVERACTIVE BLADDER. Since every human body is different, it is necessary to try different experiences. You may try one or more treatments at the same time.
Treatments for OVERACTIVE BLADDER include:
- Lifestyle changes;
- Prescription medications;
- Bladder Botox treatment;
- Nerve stimulation (peripheral and central)
- Surgery



